The Top 5 Deadliest Diseases
Conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and respiratory infections account for the majority of deaths each year around the world. Some preventive measures may help lower your risk.
When people think of the deadliest deadliest diseases in the world, their minds probably jump to the fast-acting, incurable ones that grab headlines from time to time. However, many of these types of diseases don’t rank in the top 10 causes of worldwide deaths.

An estimated 55.4 million people passed away worldwide in 2019, and 74% of these deaths were because of noncommunicable diseases, or chronic conditions that progress slowly.
Perhaps even more surprising is that several of the deadliest diseases are partially preventable. Non-preventable factors include where a person lives, access to preventive care, and quality of healthcare, all of which factor into risk.
But there are several steps that everyone can take to lower their risk.
Read on to see 10 of the deadliest diseases worldwide.
1. Ischemic heart disease, or coronary artery disease

The deadliest disease in the world is coronary artery disease (CAD).
Also called ischemic heart disease, CAD occurs when the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart become narrowed. Untreated CAD can lead to chest pain, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Impact of CAD across the world
Although it’s still the leading cause of death mortality rates have declined in many European countries and in the United States.
This may be because of better pablic health education, access to healthcare, and other forms of prevention. However, in many developing nations mortality rates for CAD are on the rise.
An increasing life span, socioeconomic changes, and lifestyle risk factors play a role in this rise.
Risk factors and prevention
Risk factors for CAD include:
- hing blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- smoking
- family history of CAD
- diabetes
- having overweight
Talk with a doctor or healthcare professional if you have one or more of these risk factors.
You can prevent CAD with medications and by taking steps to improve heart health. Some of the ways you can decrease your risk include:
- exercising regularly
- reaching or maintaining a moderate weight
- eating a balanced diet that’s that’s low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables
- avoiding smoking, if applicable
- drinking only in moderation
2. Stroke
A stroke occurs when an artery in your brain is blocked or leaks. This causes the oxygen-deprived brain cells to begin dying within minutes.
During a stroke, you feel sudden numbness and confusion or have trouble walking and seeing. If left untreated, a stroke can cause long-term disability.
In fact, strokes are the leading cause of long-term disabilities. People who receive treatment within 3 hours of having a stroke are less likely to have disabilities.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that one survey found that 93% of people knew sudden numbness on one side was a symptom of stroke. However, only 38% knew all the symptoms that would prompt them to look for emergency care.
Risk factors and prevention
Risk factors for stroke include:
- high blood pressure
- family history of stroke
- smoking, especially when combined with oral contraceptives
- being African American
- being female
Some risk factors of strokes can be lowered with preventive care, medications, and lifestyle changes. In general, good health habits can lower your risk.
Stroke prevention methods may include controlling high blood pressure with medications. You should also maintain a healthy lifestyle complete with regular exercise and a balanced diet that’s low in sodium.
If you smoke, consider quitting and drink only in moderation as these activities increase your risk of stroke.
3. Lower respiratory infections
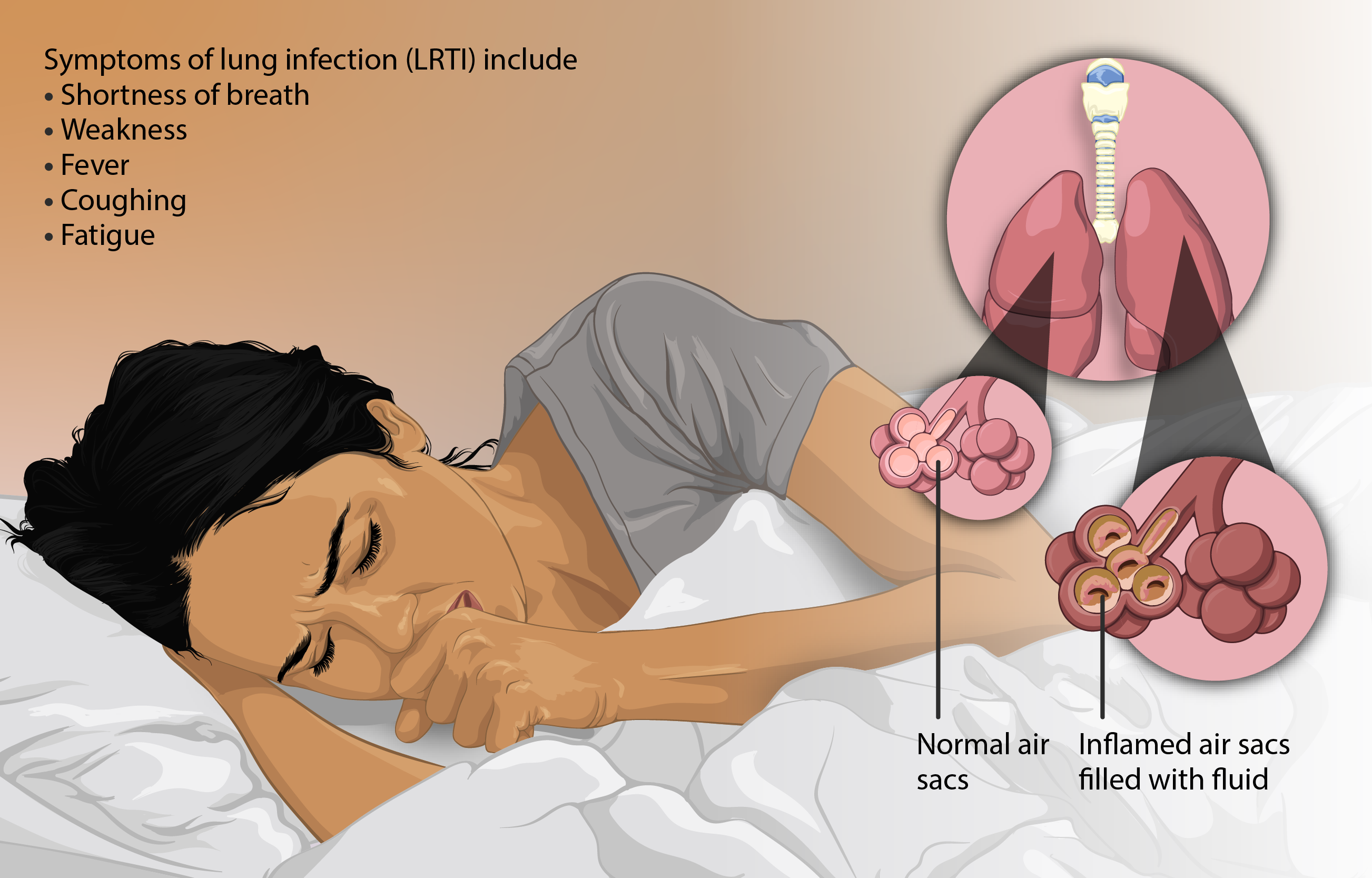
A lower respiratory infection is an infection in your airways and lungs. It can be due to:
- influenza, or the flu
- pneumonia
- bronchitis
- tuberculoses (TB)
Though viruses usually cause lower respiratory infections, they can also be caused by bacteria.
Coughing is the main symptom of a lower respiratory infection. It may produce blood sputum. You may also have a fever, sweating, or chills or experience breathlessness, wheezing, and a tight feeling in your chest.
Risk factors and prevention
Risk factors for lower respiratory infection include:
- the flu
- poor air quality or frequent exposure to lung irritants
- smoking
- a weak immune system
- crowded child care settings, which mainly affect infants
- asthma
- HlW
One of the best preventive measures you can take against lower respiratory infections is to get the shot every year. People at high risk of pneumonia can also get a vaccine.
Be sure to wash your hands regularly with soap and water to avoid transmitted bacteria, especially before touching your face or eating.
If you have a respiratory a respiratory infection, stay at home and rest until you feel better, as rest improves healing.
4. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a long-term, progressive lung disease that makes breathing difficult. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are types of COPD.
In 2018, about 16.4 million people in the United States reported a diagnosis of any type of COPD.
Risk factors and prevention
Risk factors for COPD include:
- smoking or secondhand smoke
- lung irritants such as chemical fumes
- family history, with the alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency gene being linked to COPD
- history of respiratory infections as a child
There’s no cure for COPD, but its progression can be slowed with medication.
The best ways to prevent COPD are to stop smoking, if applicable, and avoid secondhand smoke and other lung irritants. If you experience any COPD symptoms, getting treatments as soon as possible improves your outlook.
5. Trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers
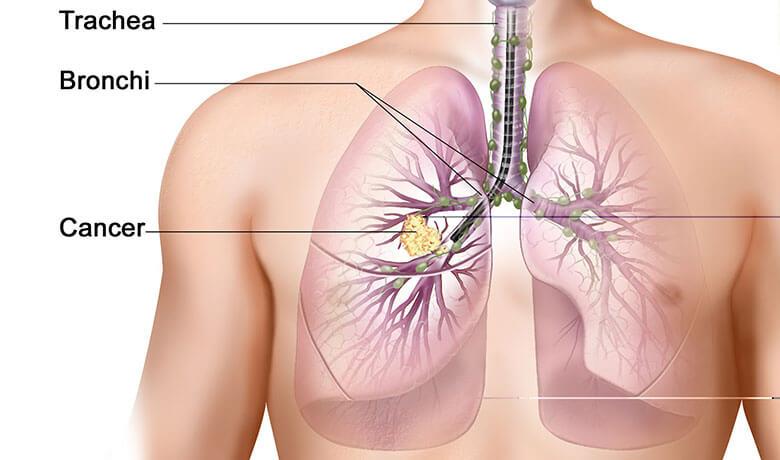
Respiratory cancers include cancers of the trachea, larynx, bronchus and lungs.
The main causes are smoking, secondhand smoke, and environmental toxins. However, household pollutions, such as fuels and mold, also contribute.
Impact of respiratory cancers around the world
A 2015 study reports that there are around 18 million new cases of lung cancer annually. In developing countries, researchers project an 81% to 100% increase in respiratory cancers because of pollution and smoking.
Many Asian countries India still use coal for cooking. Solid fuel emissions account for 17% of lung cancer deaths in males and 22% in females.
Risk factors and prevention
Trachea bronchus and lung cancers can affect anyone, but they’re most likely to affect those who have a history of smoking or tobacco use.
Other risk factors for these cancers include family history and exposure to environmental factors such as diesel fumes.
Aside from avoiding fumes and tobacco products, it isn’t known if there’s anything else that can be done to prevent lung cancers. However, routing lung scans and early detection can result in more effective treatment and an improved outlook.

